源码学习:MongoDB-ObjectId生成原理
简介
以下摘自菜鸟教程的介绍
MongoDB 是一个基于分布式文件存储的数据库
MongoDB中存储的文档必须有一个"_id"键。这个键的值可以是任何类型的,默认是个
ObjectId对象
ObjectId 是一个12字节 BSON 类型数据:
- 前4个字节表示时间戳
- 接下来的3个字节是机器标识码
- 紧接的两个字节由进程id组成(PID)
- 最后三个字节是自增随机数
按照这说法,理论上可以1s生成2^24(16777216)个,下面咱一起探究到底是否属实
源码分析
阅读源码,咱先找到源码的位置: mongodb/js-bson/objectid
在js-bson这个库中
构造函数
定位到构造函数:47-96
根据类型定义可以看出,支持传入多种类型的参数
这里,只考虑传入参数为 undefined 的情况,简化后的代码如下
const kId = Symbol('id');
class ObjectId{
static index = ~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff)
constructor(id?: string | Buffer | number | ObjectIdLike | ObjectId) {
// The most common use case (blank id, new objectId instance)
if (id == null || typeof id === 'number') {
// Generate a new id
this[kId] = ObjectId.generate(typeof id === 'number' ? id : undefined);
}
}
}const kId = Symbol('id');
class ObjectId{
static index = ~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff)
constructor(id?: string | Buffer | number | ObjectIdLike | ObjectId) {
// The most common use case (blank id, new objectId instance)
if (id == null || typeof id === 'number') {
// Generate a new id
this[kId] = ObjectId.generate(typeof id === 'number' ? id : undefined);
}
}
}首先全局会用Symbol生成一个唯一的键作为存放生成的ObjectId的key
class 上还有一个随机的静态变量 index, 这个 index 会用于自增随机数的生成,后文会看到
null == undefined结果为true,所以当我们什么都不传入的时候会调用静态方法generate生成一个新的
简化成一个js class代码的形式如下
const kId = Symbol('id');
class ObjectId{
static index = ~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff)
constructor(id) {
if (id == null || typeof id === 'number') {
this[kId] = ObjectId.generate(typeof id === 'number' ? id : undefined);
}
}
}const kId = Symbol('id');
class ObjectId{
static index = ~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff)
constructor(id) {
if (id == null || typeof id === 'number') {
this[kId] = ObjectId.generate(typeof id === 'number' ? id : undefined);
}
}
}ObjectId.generate方法生成id
庐山真面目露出来了,在这个方法里,包含了前面所说 "4" 部分结构的生成
可以看到和文档中叙述的有出入,说明咱看的文章过时了:
- 1-4字节:时间戳
- 5-9字节:进程PID(实际上是随机的5字节内容)
- 10-12字节:自增的随机数
class ObjectId {
static generate(time?: number): Buffer {
if ('number' !== typeof time) {
time = ~~(Date.now() / 1000);
}
const inc = ObjectId.getInc();
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(12);
// 4-byte timestamp
buffer.writeUInt32BE(time, 0);
// set PROCESS_UNIQUE if yet not initialized
if (PROCESS_UNIQUE === null) {
PROCESS_UNIQUE = randomBytes(5);
}
// 5-byte process unique
buffer[4] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[0];
buffer[5] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[1];
buffer[6] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[2];
buffer[7] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[3];
buffer[8] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[4];
// 3-byte counter
buffer[11] = inc & 0xff;
buffer[10] = (inc >> 8) & 0xff;
buffer[9] = (inc >> 16) & 0xff;
return buffer;
}
}class ObjectId {
static generate(time?: number): Buffer {
if ('number' !== typeof time) {
time = ~~(Date.now() / 1000);
}
const inc = ObjectId.getInc();
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(12);
// 4-byte timestamp
buffer.writeUInt32BE(time, 0);
// set PROCESS_UNIQUE if yet not initialized
if (PROCESS_UNIQUE === null) {
PROCESS_UNIQUE = randomBytes(5);
}
// 5-byte process unique
buffer[4] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[0];
buffer[5] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[1];
buffer[6] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[2];
buffer[7] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[3];
buffer[8] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[4];
// 3-byte counter
buffer[11] = inc & 0xff;
buffer[10] = (inc >> 8) & 0xff;
buffer[9] = (inc >> 16) & 0xff;
return buffer;
}
}下面先介绍一下代码中 Buffer 相关的内容:
Buffer.alloc(size[, fill[, encoding]]):在内存中开辟一块指定字节数的连续空间,用于二进制数据存放,默认使用0进行填充- buffer数组可以像普通数组一样使用直接赋值
Buffer.writeUInt32BE(value[, offset]):将值按32位无符号证书数写入到buffer中,第二个参数位偏移的字节数(由于是32位整数,这里offset必须是 4 的整倍数)
简单演示writeUInt32BE的作用
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(8)
// <Buffer 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00>
// 0x开头表示16进制数
buffer.writeUInt32BE(0xff,0)
// <Buffer 00 00 00 ff 00 00 00 00>
buffer.writeUInt32BE(255,4)
// <Buffer 00 00 00 ff 00 00 00 ff>const buffer = Buffer.alloc(8)
// <Buffer 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00>
// 0x开头表示16进制数
buffer.writeUInt32BE(0xff,0)
// <Buffer 00 00 00 ff 00 00 00 00>
buffer.writeUInt32BE(255,4)
// <Buffer 00 00 00 ff 00 00 00 ff>下面简单介绍一下进制转换知识,帮助理解源码
进制转换
// 生成一个12字节的连续空间
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(12)
// <Buffer 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00>// 生成一个12字节的连续空间
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(12)
// <Buffer 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00>1字节(Byte)等于 8 比特(Bit - 二进制位),存储范围为 0 至 2^8-1 即 0 - 255,共 256 个数字
其中每个buffer的内容由 2个16 进制位表示(00至ff)
二进制位 0 0 0 0
对应位值(10进制) 8 4 2 1二进制位 0 0 0 0
对应位值(10进制) 8 4 2 1举例(看一下上面对应的值)
二进制 0 1 0 1
# 等价
十进制 5 = 0 + 4 + 0 + 1
# 等价
十六进制 5二进制 0 1 0 1
# 等价
十进制 5 = 0 + 4 + 0 + 1
# 等价
十六进制 5二进制 1 1 0 1
# 等价
十进制 13 = 8 + 4 + 0 + 1
# 等价
十六进制 d二进制 1 1 0 1
# 等价
十进制 13 = 8 + 4 + 0 + 1
# 等价
十六进制 dBuffer存储数字示例(将自动进行进制转换):
const buf = Buffer.alloc(1)
buf[0] = 12
// <Buffer 0c>
buf[0] = 15
// <Buffer 0f>
buf[0] = 255
// <Buffer ff>const buf = Buffer.alloc(1)
buf[0] = 12
// <Buffer 0c>
buf[0] = 15
// <Buffer 0f>
buf[0] = 255
// <Buffer ff>下面回到正题
时间戳的生成
使用Date.now()获取当前时间,除1000后取整
- ~ : 是位运算符 取反
- 位运算符都是对二进制进行操作
- ~~:连续两次取反操作达到取整目的,正数的行为与
Math.floor一致,附属行为与Math.ceil一致
console.log(~~(12.5)) // 12
console.log(Math.floor(12.5)) // 12
console.log(~~(-12.5)) // -12
console.log(Math.ceil(-12.5)) // -12console.log(~~(12.5)) // 12
console.log(Math.floor(12.5)) // 12
console.log(~~(-12.5)) // -12
console.log(Math.ceil(-12.5)) // -12时间戳的获取
const time = ~~(Date.now() / 1000);const time = ~~(Date.now() / 1000);存入前4字节
// 4-byte timestamp
buffer.writeUInt32BE(time, 0);// 4-byte timestamp
buffer.writeUInt32BE(time, 0);随机的“进程PID”生成
可以看到这里是用的randomBytes方法生成的一个5字节的随机数
import {randomBytes} from './parser/utils'
PROCESS_UNIQUE = randomBytes(5);import {randomBytes} from './parser/utils'
PROCESS_UNIQUE = randomBytes(5);randomButes精简后的内容如下
// parser/utils
const detectRandomBytes = (): RandomBytesFunction => {
if (typeof global !== 'undefined' && global.crypto && global.crypto.getRandomValues) {
return size => global.crypto.getRandomValues(Buffer.alloc(size));
}
let requiredRandomBytes: RandomBytesFunction | null | undefined;
try {
requiredRandomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes;
} catch (e) {
}
return requiredRandomBytes || insecureRandomBytes;
};
export const randomBytes = detectRandomBytes();// parser/utils
const detectRandomBytes = (): RandomBytesFunction => {
if (typeof global !== 'undefined' && global.crypto && global.crypto.getRandomValues) {
return size => global.crypto.getRandomValues(Buffer.alloc(size));
}
let requiredRandomBytes: RandomBytesFunction | null | undefined;
try {
requiredRandomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes;
} catch (e) {
}
return requiredRandomBytes || insecureRandomBytes;
};
export const randomBytes = detectRandomBytes();经过测试实际上调用的是require('crypto').randomBytes
即如下代码,调用的Node内置的crypto库提供的方法
TODO:下次出文介绍一下这个require('crypto').randomBytes
export const randomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes;export const randomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes;最终生成这5个字节的代码如下
const randomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes;
const PROCESS_UNIQUE = randomBytes(5);
// 5-byte process unique
buffer[4] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[0];
buffer[5] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[1];
buffer[6] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[2];
buffer[7] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[3];
buffer[8] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[4];const randomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes;
const PROCESS_UNIQUE = randomBytes(5);
// 5-byte process unique
buffer[4] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[0];
buffer[5] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[1];
buffer[6] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[2];
buffer[7] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[3];
buffer[8] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[4];自增的随机数
class ObjectId {
static index = ~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff)
static getInc(): number {
return (ObjectId.index = (ObjectId.index + 1) % 0xffffff);
}
static generate(time?: number): Buffer {
const inc = ObjectId.getInc();
// 省略中间无关代码
// 3-byte counter
// 存入最后2字节
buffer[11] = inc & 0xff;
// 右移8位然后,低位的2字节存入第11位
buffer[10] = (inc >> 8) & 0xff;
// 右移16位,低位的2字节存入第10位
buffer[9] = (inc >> 16) & 0xff;
return buffer;
}
}class ObjectId {
static index = ~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff)
static getInc(): number {
return (ObjectId.index = (ObjectId.index + 1) % 0xffffff);
}
static generate(time?: number): Buffer {
const inc = ObjectId.getInc();
// 省略中间无关代码
// 3-byte counter
// 存入最后2字节
buffer[11] = inc & 0xff;
// 右移8位然后,低位的2字节存入第11位
buffer[10] = (inc >> 8) & 0xff;
// 右移16位,低位的2字节存入第10位
buffer[9] = (inc >> 16) & 0xff;
return buffer;
}
}- 生成一个3字节的随机数
~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff) - 自增1后,作为最终的随机数
精简ObjectId实现
拆解完后上面的ObjectId,真实的 3 部分后,依葫芦画瓢实现一个最小可行的方法
const randomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes
const kId = Symbol('id');
let PROCESS_UNIQUE = null;
class MyObjectId {
static index = ~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff)
constructor(id) {
if (id == null || typeof id === 'number') {
this[kId] = MyObjectId.generate(typeof id === 'number' ? id : undefined);
}
}
static getInc() {
return (MyObjectId.index = (MyObjectId.index + 1) % 0xffffff);
}
static generate(time) {
if ('number' !== typeof time) {
time = ~~(Date.now() / 1000);
}
const inc = MyObjectId.getInc();
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(12);
// 4-byte timestamp
buffer.writeUInt32BE(time, 0);
// set PROCESS_UNIQUE if yet not initialized
if (PROCESS_UNIQUE === null) {
PROCESS_UNIQUE = randomBytes(5);
}
// 5-byte process unique
buffer[4] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[0];
buffer[5] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[1];
buffer[6] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[2];
buffer[7] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[3];
buffer[8] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[4];
// 3-byte counter
buffer[11] = inc & 0xff;
buffer[10] = (inc >> 8) & 0xff;
buffer[9] = (inc >> 16) & 0xff;
return buffer;
}
toHexString(){
return this[kId].toString('hex')
}
}
module.exports = {
MyObjectId
}const randomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes
const kId = Symbol('id');
let PROCESS_UNIQUE = null;
class MyObjectId {
static index = ~~(Math.random() * 0xffffff)
constructor(id) {
if (id == null || typeof id === 'number') {
this[kId] = MyObjectId.generate(typeof id === 'number' ? id : undefined);
}
}
static getInc() {
return (MyObjectId.index = (MyObjectId.index + 1) % 0xffffff);
}
static generate(time) {
if ('number' !== typeof time) {
time = ~~(Date.now() / 1000);
}
const inc = MyObjectId.getInc();
const buffer = Buffer.alloc(12);
// 4-byte timestamp
buffer.writeUInt32BE(time, 0);
// set PROCESS_UNIQUE if yet not initialized
if (PROCESS_UNIQUE === null) {
PROCESS_UNIQUE = randomBytes(5);
}
// 5-byte process unique
buffer[4] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[0];
buffer[5] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[1];
buffer[6] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[2];
buffer[7] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[3];
buffer[8] = PROCESS_UNIQUE[4];
// 3-byte counter
buffer[11] = inc & 0xff;
buffer[10] = (inc >> 8) & 0xff;
buffer[9] = (inc >> 16) & 0xff;
return buffer;
}
toHexString(){
return this[kId].toString('hex')
}
}
module.exports = {
MyObjectId
}测试
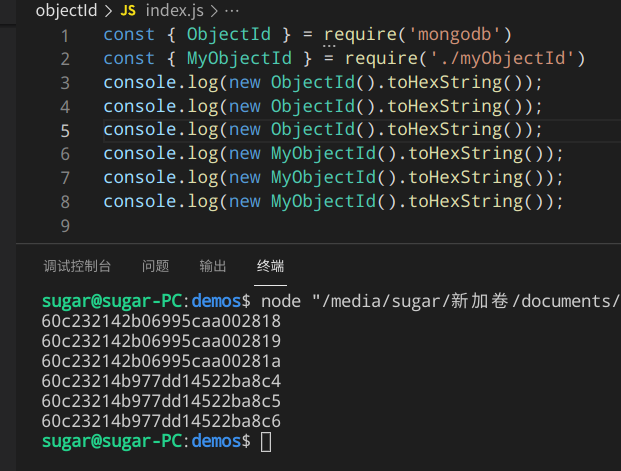
const { ObjectId } = require('mongodb')
const { MyObjectId } = require('./myObjectId')
console.log(new ObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new ObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new ObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new MyObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new MyObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new MyObjectId().toHexString());const { ObjectId } = require('mongodb')
const { MyObjectId } = require('./myObjectId')
console.log(new ObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new ObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new ObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new MyObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new MyObjectId().toHexString());
console.log(new MyObjectId().toHexString());结果如下,符合预期
总结
网上的部分翻译资料确实有些过时了
抽时间看看简单的源码,还是有助于温习自己所学的知识
通过阅读优秀的源码,有助于加快修炼
位运算符虽在开发中用得不多,但很多优秀的库中都有,提醒自己下来还是多熟悉一下,看看能否用在计算场景中,提升计算效率
TODO:搞一篇位运算的文章,学习一下优秀开源库中的用法
 德沃编程
德沃编程